It is the equation of a circle Probably you can recognize it as the equation of a circle with radius r=1 and center at the origin, (0,0) The general equation of the circle of radius r and center at (h,k) is (xh)^2(yk)^2=r^2 How to find the center, radius, and equation of the sphere The formula for the equation of a sphere We can calculate the equation of a sphere using the formula ( x − h) 2 ( y − k) 2 ( z − l) 2 = r 2 (xh)^2 (yk)^2 (zl)^2=r^2 ( x − h) 2 ( y − k) 2 ( z − l) 2 = r 2 where ( h, k, l) (h,k,l) ( h, k, l) is the center ofSolution to Problem Set #9 1 Find the area of the following surface (a) (15 pts) The part of the paraboloid z = 9 ¡ x2 ¡ y2 that lies above the x¡y plane ±4 ±2 0 2 4 x ±4 ±2 0 2 4 y ±4 ±2 0 2 4 Solution The part of the paraboloid z = 9¡x2 ¡y2 that lies above the x¡y plane must satisfy z = 9¡x2 ¡y2 ‚ 0 Thus x2 y2 • 9 We
Graph It Aka Graph It Ii Schaubild Aka Graph It Enhanced Atarinside
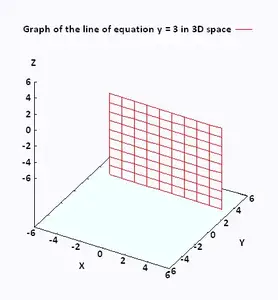
Z=3-x^2-y^2 graph
Z=3-x^2-y^2 graph-The graph of a function f(x;y) = 8 x2 y) So, one surface we could use is the part of the surface z= 8 x 2 yinside the cylinder x2 y = 1 (right picture) 4 x y z x y z Let's call this surface Sand gure out how it should be oriented The original curve was parameterizedIn the following graph, the region D D is situated below y = x y = x and is bounded by x = 1, x = 5, x = 1, x = 5, and y = 0 y = 0 133 In the following graph, the region D D is bounded by y = x y = x and y = x 2 y = x 2 In the following exercises, evaluate the double integral



Surfaces Part 3
X^2y^2z^2=1 WolframAlpha Have a question about using WolframAlpha?Take the square root of both sides of the equation x^ {2}y^ {2}z^ {2}=0 Subtract z^ {2} from both sides y^ {2}x^ {2}z^ {2}=0 Quadratic equations like this one, with an x^ {2} term but no x term, can still be solved using the quadratic formula, \frac {b±\sqrt {b^ {2}4ac}} {2a}, once they are put in standard form ax^ {2}bxc=0Surfaces and Contour Plots Part 4 Graphs of Functions of Two Variables The graph of a function z = f(x,y) is also the graph of an equation in three variables and is therefore a surfaceSince each pair (x,y) in the domain determines a unique value of z, the graph of a function must satisfy the "vertical line test" already familiar from singlevariable calculus
Definition In the cylindrical coordinate system, a point in space (Figure 2) is represented by the ordered triple (r,θ,z),(r,θ,z),where (r,θ)(r,θ)are the polar coordinates of the point's projection in the xyplane zzis the usual zcoordinatezcoordinatein the Cartesian coordinate systemThe graph of D is y=−x x y y=x 18 f(x;y) = p x2 y2 1ln(4 x2 y2) Solution For the domain of f we need x2y2 1 0, ie, x2y2 1 and 4 x2 y2 > 0, ie, x2 y2 < 4 So D = f(x;y)j1 x2 y2 < 4g 4 x y 1 5ASSIGNMENT 8 SOLUTION JAMES MCIVOR 1 Stewart 5 pts Find the volume of the solid region bounded by the paraboloids z = 3x2 3y2 and z= 4 x 2 y Solution
6 (17 points) Evaluate the integral by changing to spherical coordinates Z 4 0 Zp 16 2y p 16 y2 Zp 16 x2 y2 0 (x2 y2 z2)zdzdxdy Solution Z 4 0 Zp 16 2y p 16 y2 Zp 16 x2 y2 0 (x 2y2 z 2)zdzdxdy= Z ˇ 0 Z ˇ=2My Multiple Integrals course https//wwwkristakingmathcom/multipleintegralscourseLearn how to use double integrals to find the volume of the solid tha(xyz)^3 (x y z) (x y z) (x y z) We multiply using the FOIL Method x *




How To Generate And Draw Simple Bipartite Graphs Newbedev



12 6 Quadric Surfaces Mathematics Libretexts
Steps to graph x^2 y^2 = 4Solutions to Homework 9 Section 127 # 12 Let Dbe the region bounded below by the cone z= p x 2 y2 and above by the paraboloid z= 2 x y2Setup integrals in cylindrical coordinates which compute the volume of DThis video explains how to represent the intersection of two surfaces as a vector valued functionhttp//mathispower4uyolasitecom/



Consider Minimize Z 3x 2y Subject To X Y 8 3x 5




Ex 12 1 Q4 Minimize Z 3x 5y Such That X 3y 3 X Y 2 X Y 0
Z=sqrt (x^2y^2) WolframAlpha Volume of a cylinder? Take any Pythagorean triplet (a, b, c) Multiplying c6k − 2, where k is a natural number As an alternative, you can take any standard Pythagorean triple, eg 32 42 = 52, and then multiply through by 54 to get which will give an infinite set of solutions x = a3 − 3ab2, y = 3a2b − b3, z = a2 b2 In this case the surface area is given by, S = ∬ D √f x2f y2 1dA S = ∬ D f x 2 f y 2 1 d A Let's take a look at a couple of examples Example 1 Find the surface area of the part of the plane 3x 2yz =6 3 x 2 y z = 6 that lies in the first octant Show Solution Remember that the first octant is the portion of the



最も選択された Y X2 2 Graph ニスヌーピー 壁紙



What Is The Graph Of 2x Y Z 3 Socratic
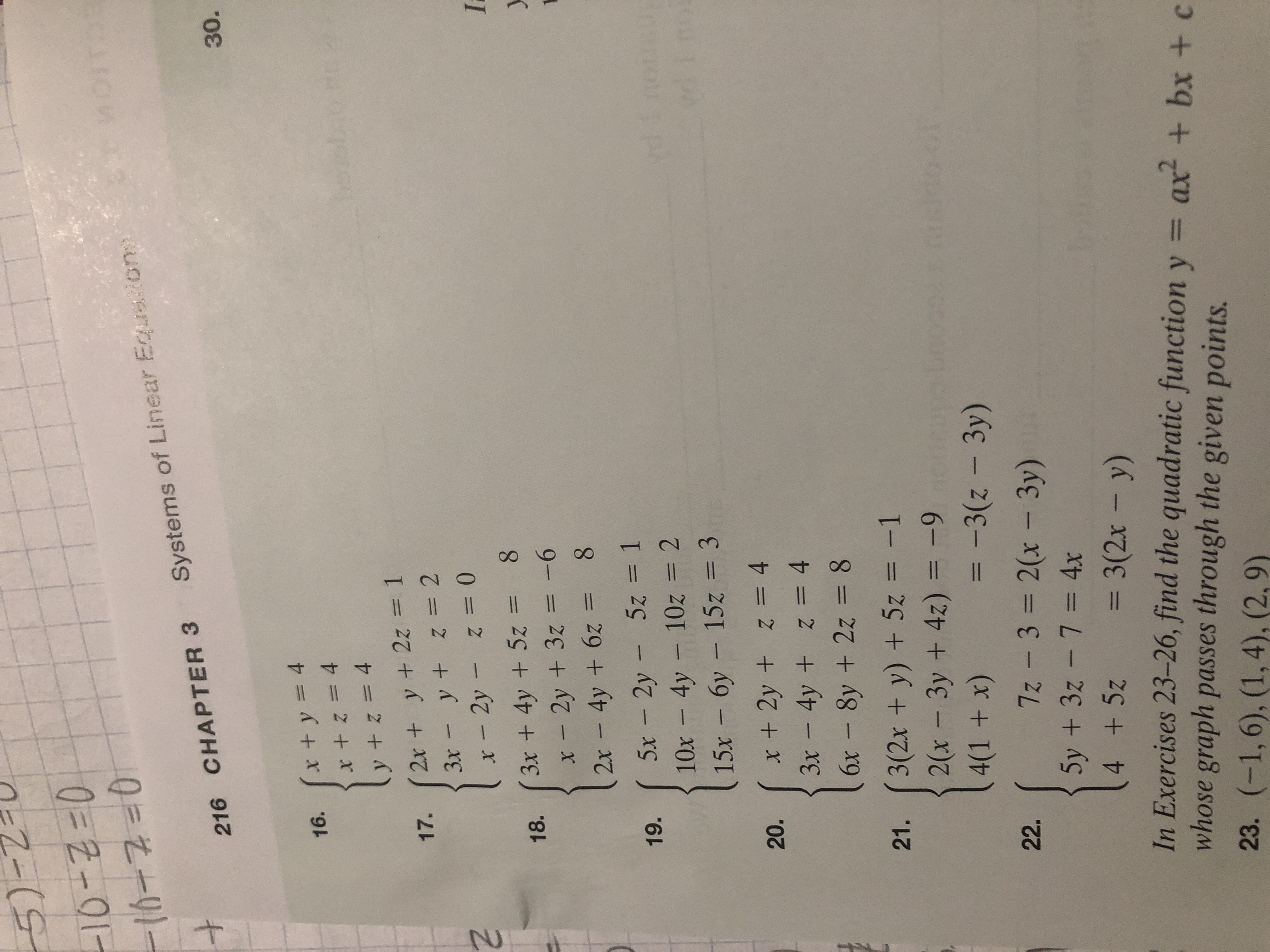
3D Function Grapher To use the application, you need Flash Player 6 or 7 Click below to download the free player from the Macromedia site Download Flash Player 7Calculus questions and answers;This tool graphs z = f(x,y) mathematical functions in 3D It is more of a tour than a tool All functions can be set different boundaries for x, y, and z, to maximize your viewing enjoyment This tool looks really great with a very high detail level, but you may find it more comfortable to use less detail if you want to spin the model



Graph It Aka Graph It Ii Schaubild Aka Graph It Enhanced Atarinside



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
(1 point) Find the point on the graph of z(3x2 y2) at which vector n 〈24,2,1) is normal to the tangent plane (3x2 Get more help from Chegg Solve itNot a problem Unlock StepbyStep z=x^2y^2 Extended Keyboard ExamplesConsider x^ {2}y^ {2}xy22xy as a polynomial over variable x Find one factor of the form x^ {k}m, where x^ {k} divides the monomial with the highest power x^ {2} and m divides the constant factor y^ {2}y2 One such factor is xy1 Factor the polynomial by dividing it by this factor




Algebra 2 Chapter 3 Notes Systems Of Linear Equalities And Inequalities Algebra 2 Chapter 3 Notes Systems Of Linear Equalities And Inequalities Ppt Download



1
Here is the graph of the surface and we've tried to show the region in the \(xy\)plane below the surface Here is a sketch of the region in the \(xy\)plane by itself By setting the two bounding equations equal we can see that they will intersect at \(x = 2\) and \(x = 2\)Butler CC Math Friesen (traces) Elliptic paraboloid z = 4x2 y2 2 2 2 Ax By Cz Dx Ey F = 0 Quadric Surfaces Example For the elliptic paraboloid z = 4x2 y2 xy trace set z = 0 →0 = 4x2 y2 This is point (0,0) yz trace set x = 0 →z = y2 Parabola in yz plane xz trace set y = 0 →y = 4x2 Parabola in xz plane Trace z = 4 parallel to xy plane Set z = 4 →4 = 4x2 y2For the cone z = 3 (x 2 y 2) z = 3 (x 2 y 2) or A graph of our balloon model and a crosssectional diagram showing the dimensions are shown in the following figure Figure 562 (a) Use a half sphere to model the top part of the balloon and a frustum of a cone to model the bottom part of the balloon (b) A cross section of the balloon



Tschirnhausen Cubic
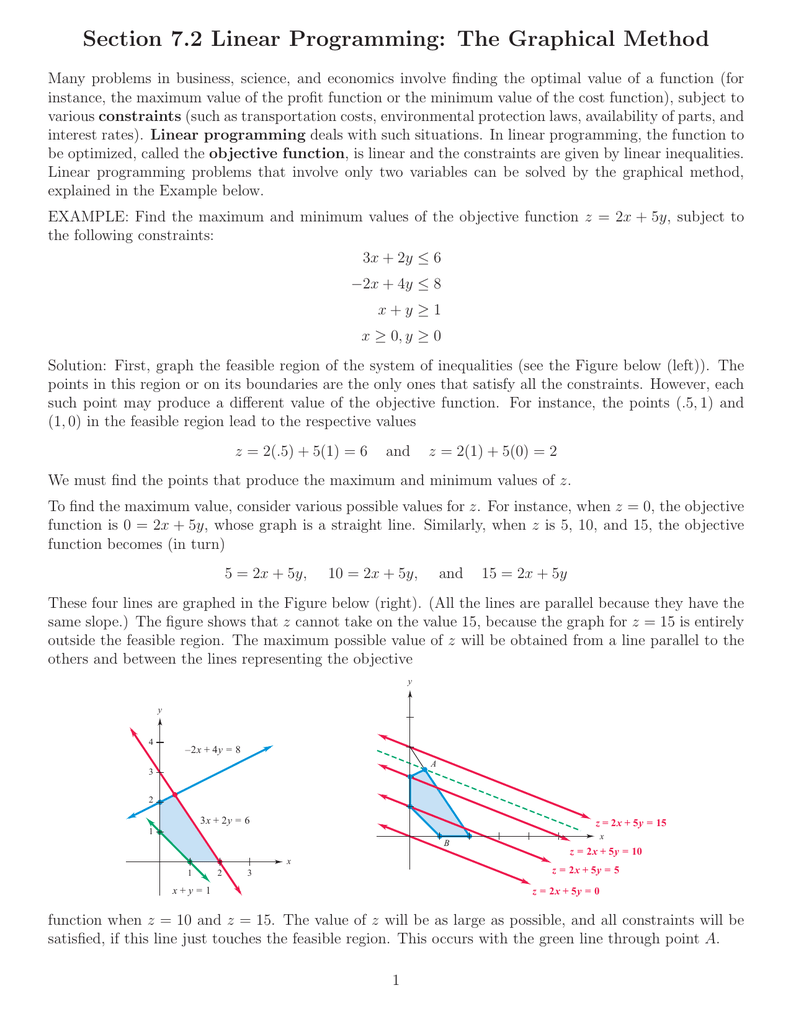



Section 7 2 Linear Programming The Graphical Method
Plotting graphics3d Share Improve this question Follow asked Nov 29 '15 at 533 user user 11 1 1 gold badge 1 1 silver badge 2 2 bronze badgesPlot z=x^2y^2 WolframAlpha Assuming "plot" is a plotting function Use as referring to geometry insteadRelated » Graph » Number Line » Examples » Our online expert tutors can answer this problem Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes



Level Sets Math Insight




Surfaces Part 3
Dx = " x5 15 − x8 24 # 2 0 = 32 15 − 256 24 = − 128 15 07 Example Evaluate Z π π/2See the answer Find the POINT on the graph of z = 3x^2 − 4y^2 at which the vector n = < 3, 5, 4 > is normal to the tangent planePlane z = 1 The trace in the z = 1 plane is the ellipse x2 y2 8 = 1



Answer In Geometry For Tarynn Wiese
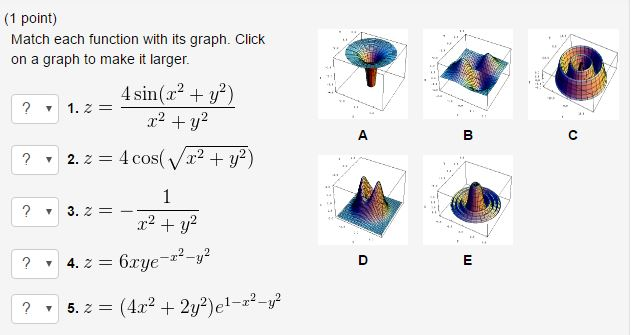



Match Each Function With Its Graph Click On A Graph Chegg Com
Contact Pro Premium Expert Support » How to plot 3 dimensional graph for x^2 y^2 = 1?Graph x^2y^2=1 x2 − y2 = −1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Find the standard form of the hyperbola Tap for more steps Flip the sign on each term of the equation so the term on the right side is positive − x 2 y 2 = 1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Simplify each term in the equation in order to set the right side equal to 1 1 The standard form of an




X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Graph Novocom Top




Minimise And Minise Z 3x 4y Subject To X 2y Le 0 3x Y Le 4 X
Mathematics The graph of y (x) is transformed to give the graph of y=f (x3) The point A on the graph of y=f (x) is mapped to the point P on the graph of y= f (x3) The coordinates of point A are (9,1) Find the coordinates of point P You can view more similar questions or ask a new questionSketch a graph of each surface Then, match each surface to its brief description in words x = 4 z = 3 x2 y2 z2 = 36 3x 6y 5z = 4 z = 3y2 z2 = x2 36y2 z = x2 49y2 3 x2 y2 = 36 z = 16x2 y2 Circular cylinder Sphere Parabolic cylinder Elliptic paraboloid Horizontal plane Skew line Circle Vertical plane Sinusoidal cylinderPiece of cake Unlock StepbyStep Extended Keyboard Examples
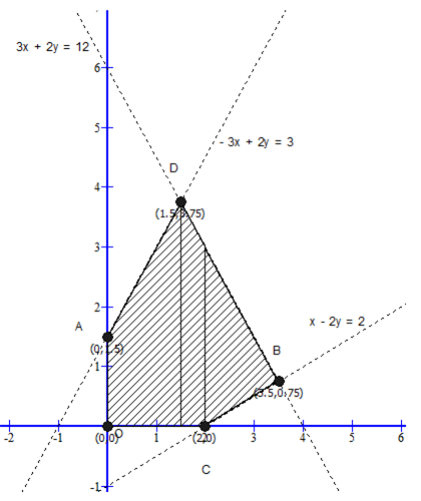



Minimum And Maximum Z 5x 2y Subject To The Following Constraints X 2y 2 3x 2y 12 3x 2y 3 X 0 Y 0 From Mathematics Linear Programming Class 12 Cbse




Graph It Aka Graph It Ii Schaubild Aka Graph It Enhanced Atarinside
I am having trouble expressing the titular question as iterated integrals over a given region I have tried narrowing down the problem, and have concluded that the simplest way to approach this is to06 Example Evaluate Z 2 0 Z x x2 y2xdydx Solution integral = Z 2 0 Z x x2 y2xdydx Z 2 0 " y3x 3 # y=x y=x2 dx = Z 2 0 x4 3 − x7 3!(e) Below is the graph of z = x2 y2 On the graph of the surface, sketch the traces that you found in parts (a) and (c) For problems 1213, nd an equation of the trace of the surface in the indicated plane Describe the graph of the trace 12 Surface 8x 2 y z2 = 9;




I Can T Use Ggtern To Draw Graph General Rstudio Community



Y 2 Z 2 16 Is This Represents A Circle In 3 Dimensional Space Or 2 Dimensional Space Socratic
Problems Flux Through a Paraboloid Consider the paraboloid z = x 2 y 2 Let S be the portion of this surface that lies below the plane z = 1Quadric surfaces are the graphs of quadratic equations in three Cartesian variables in space Like the graphs of quadratics in the plane, their shapes depend on the signs of the various coefficients in their quadratic equations Spheres and Ellipsoids A sphere is the graph of an equation of the form x 2 y 2 z 2 = p 2 for some real number p The treewidth of a graph is an important invariant in structural and algorithmic graph theory This paper studies the treewidth of line graphsWe show that determining the treewidth of the line graph of a graph G is equivalent to determining the minimum vertex congestion of an embedding of G into a tree Using this result, we prove sharp lower bounds in
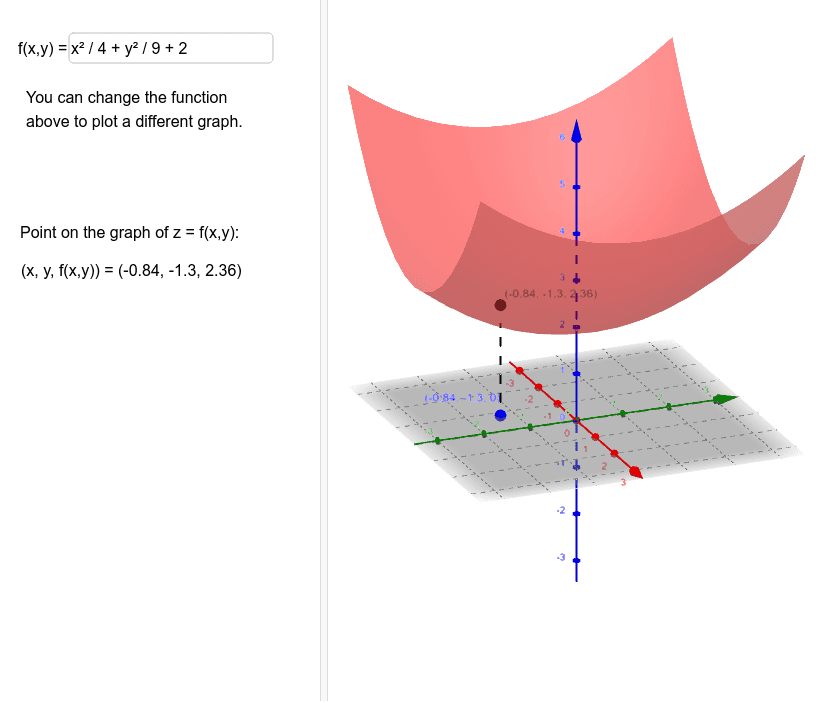



Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra




Chapter Applications Of The Derivative
C A Bouman Digital Image Processing 2 Properties of Chromaticity Coordinates x = X X Y Z y = Y X Y Z z = Z X Y Z • xyz =1 A quick video about graphing 3d for those who never done it before Pause the video and try itThe intersection with a plane x= kis z= siny, the graph of sine function It does not depend on the intersection plane x= k, so it is a cylinder whose base is a sine curve 1 MATH 04 Homework Solution HanBom Moon 1269(a)Find and identify the traces of the quadric surface x2 y2 z2 = 1



Instructional Unit The Parabola Day 8




Solution Of Lpp By Graphical Method Linear Programming Problem
The origin of Z 0 comes from the spilling of the electron wavefunction out of the surface As a result, the position of image plane representing the reference for the space coordinate is different from the substrate surface itself and modified by Z 0 Table 1 shows the jellium model calculation for van der Waals constant C v and dynamical image plane Z 0 of rare gas atoms on various Example 1586 Setting up a Triple Integral in Spherical Coordinates Set up an integral for the volume of the region bounded by the cone z = √3(x2 y2) and the hemisphere z = √4 − x2 − y2 (see the figure below) Figure 15 A region bounded below by a cone and above by a hemisphere SolutionI am already using it and I only can plot in 2 dimensional graph Can someone help me with this problem?



Principles Of Mathematical Economics Ii Solutions Manual Supplementary Materials And Supplementary Exercises Shapoor Vali Pdf Free Download




Match The Graph To The Equation 1 X 2 1 X 2 Y 2 2 Z 2 9 X 2 Y 2 3 X 1 Y 2 Z 2 4 X Sqrt Y 2 Z 2 5 Z
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreQuestion Find The POINT On The Graph Of Z = 3x^2 − 4y^2 At Which The Vector N = < 3, 5, 4 > Is Normal To The Tangent Plane This problem has been solved!Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history



Surfaces Part 2
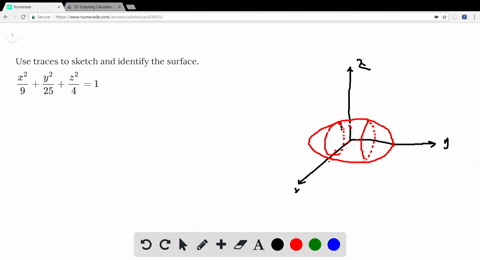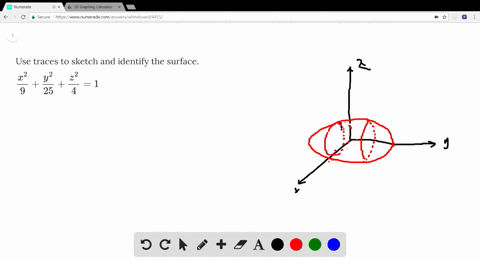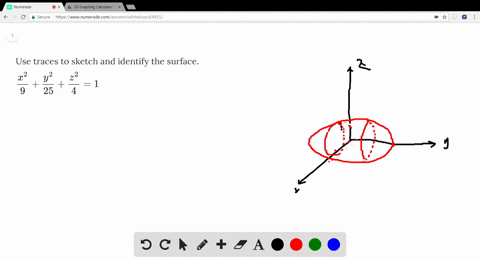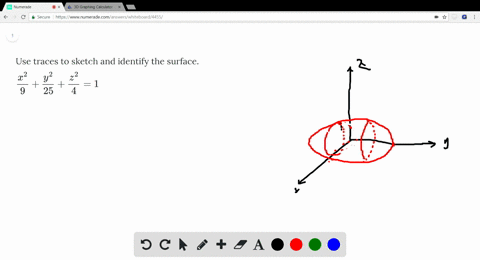



Solved Use Traces To Sketch And Identify The Surf
Free online 3D grapher from GeoGebra graph 3D functions, plot surfaces, construct solids and much more!Answer by lenny460 (1073) ( Show Source ) You can put this solution on YOUR website!



What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora




Ex 12 1 9 Maximise Z X 2y Subject To X 3 X Y 5
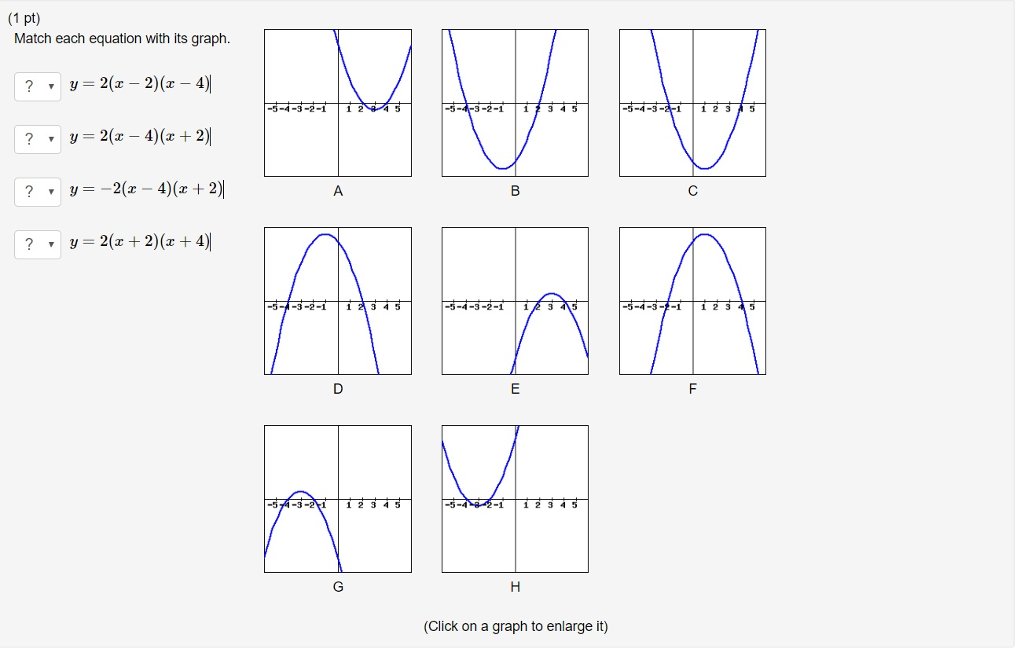



1 Pt Match Each Equation With Its Graph 2 2 4 3 Chegg Com



Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers




Triple Integrals In Spherical Coordinates Z Sqrt 3x 2 3y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Walking Randomly A Little Mathematics For Valentine S Day



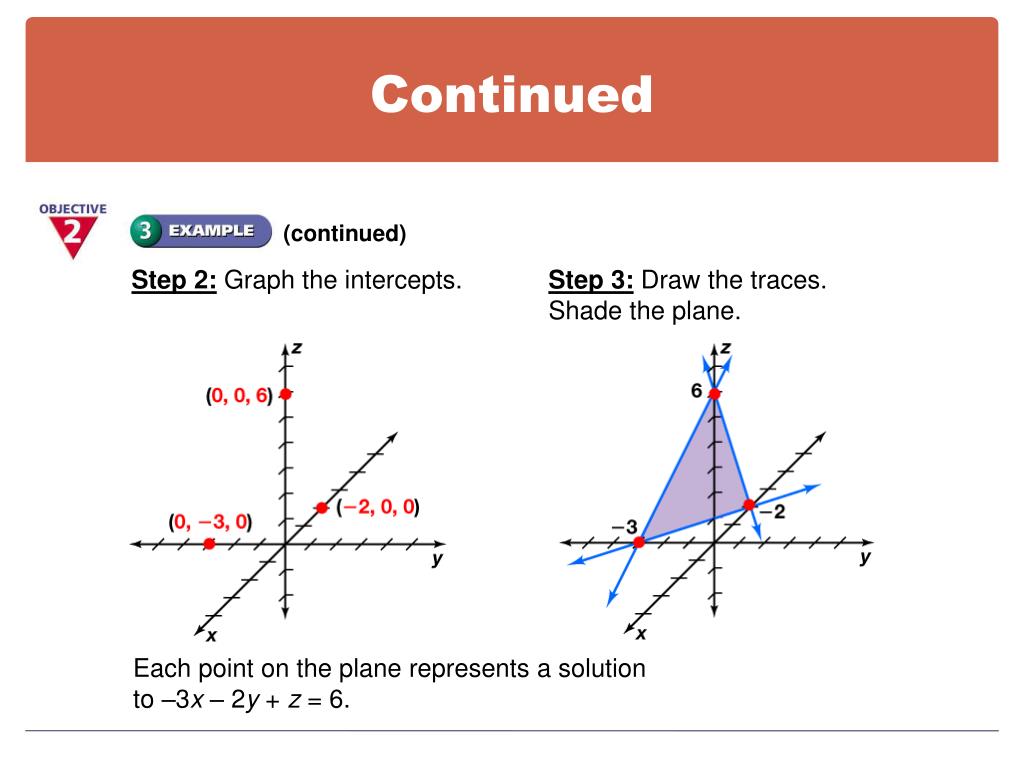
Plot The Intercepts And Sketch A Graph Of The Plane 3x 2y 3z 6 Homework Help And Answers Slader



If You Type Out An Equation Into Google It Gives You The 3d Graph Of The Equation Mildlyinteresting



How Do You Graph Z Y 2



Solution Find The Maximun Value Of Z 3x 2y Subject Tothe Contraints X Gt 0 Y Gt 0 X 2y Lt 4 X Y Lt 1



Solved Graph Each System Of Inequalities Name The Coordinates Of The Vertices Of The Feasible Region Find The Maximum And Minimum Values Of The G Course Hero



3d Surface Plotter Academo Org Free Interactive Education




Oneclass Graph The System Of Linear Equations Solve The System And Interpret Your Answer 2x Y




Writing And Graphing Linear Equations Pdf Pdf Document




Minimise Z 3x 4y Subject To X 2yle8 3x 2yle12 Xge0 Yge0




Matlab Tutorial




Enm1600 13 Module Notes 3 Functions And Relations Questions Studocu



Answered 0 Is Cnte Raph Costai Function 229en Bartleby



Ppt 3 5 Graphs In Three Dimensions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
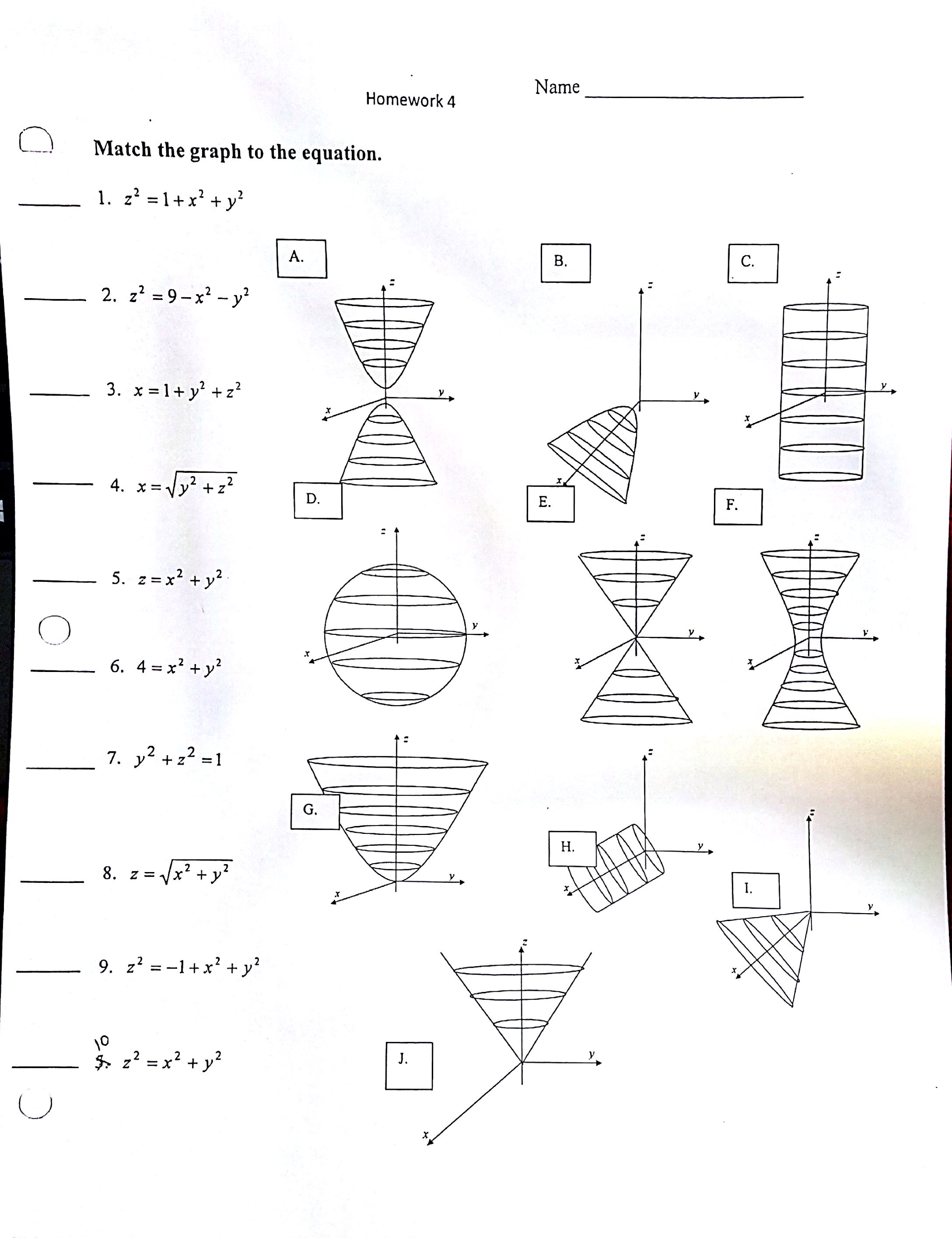



Match The Graph To The Equation X 2 1 X 2 Y 2 Chegg Com




Finding Volume Of Solid Under Z Sqrt 1 X 2 Y 2 Above The Region Bounded By X 2 Y 2 Y 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Find The Maximum And Minimum Values Of Z 2x Y Subject To The Constraints X 3y 6 X 3y 3 3x 4y 24 3x 2y 6 5x Y 5 X 0 And Y 0




Complex Numbers Absolute Value




Matlab Tutorial




How To Plot X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
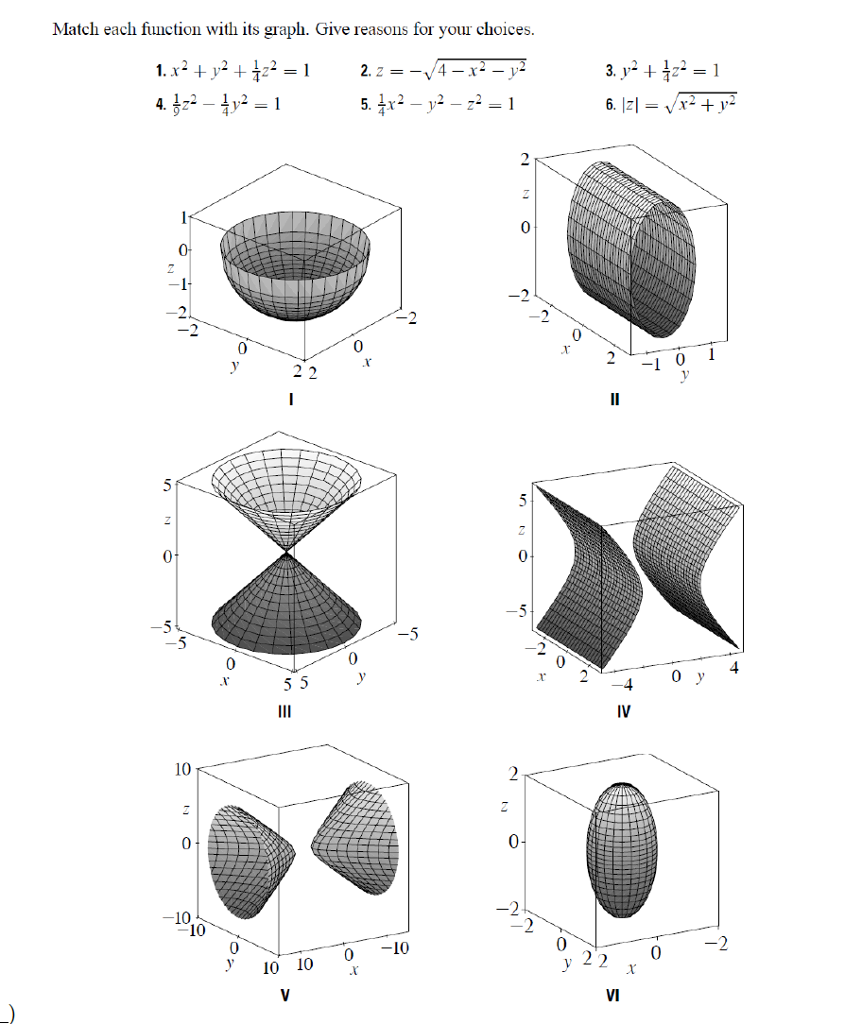



Match Each Function With Its Graph Give Reasons For Chegg Com




Find The Volume Of The Region Bounded By The Paraboloids Z X 2 Y 2 And Z 36 3x 2 3y 2 Study Com



Graph Of Z X 2 Y 2 Download Scientific Diagram




Solve The Following Linear Programming Problem Graphically Maximise Z X 2y Subject To The Constraints X 3 X Y 5 X 2 Y 6 Y 0 From Linear Programming Class 12 Cbse




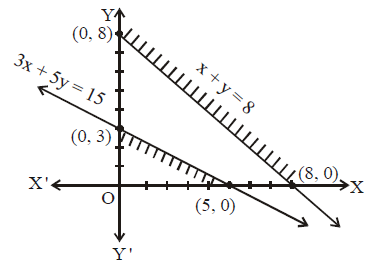
Minimise Z 3x 2y Subject To The Constraints X Y 8 1 3x 5y 15 2 X 0 Y 0 3




Graph Of Z 1 X 2 Y 2 Novocom Top




Saddle Point Wikipedia



Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables




Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube




Draw The Graph Of Y 3x 2 Brainly In




14 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts



Minimize Z 3x 2y Subject To The Constraints X Y 8 3x 5y 15 And X 0 Y 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
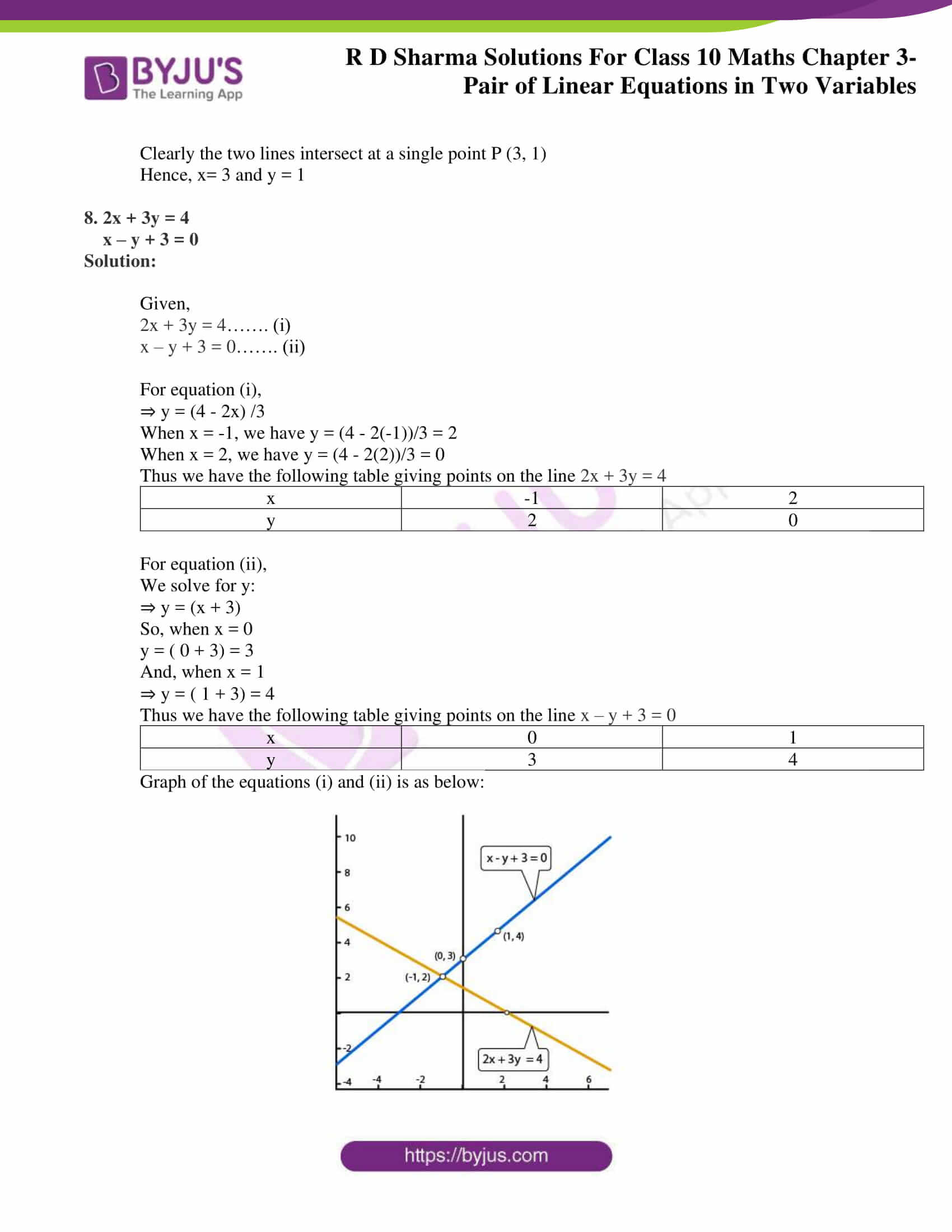



Rd Sharma Class 10 Solutions Maths Chapter 3 Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Exercise 3 2



1




C54h4oanl8ccgm



Solution Find The Maximum Value Of The Objective Function Z 3x 5y Subject To The Folloing Constraints X Greater Than Or Equal To 2 Y Greater Than Or Equal To 0 X Y Less Than



Determine The Minimum Value Of Z 3x 2y If Any If The Feasible Region For An Lpp Is Shown In Fig 12 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Graph The Cylinder X 2 Y 2 16 And The Sphere X 2 Y 2 Z 2 49 Together Using Maple And Find The Volume Outside The Cylinder And Inside The Sphere Study Com
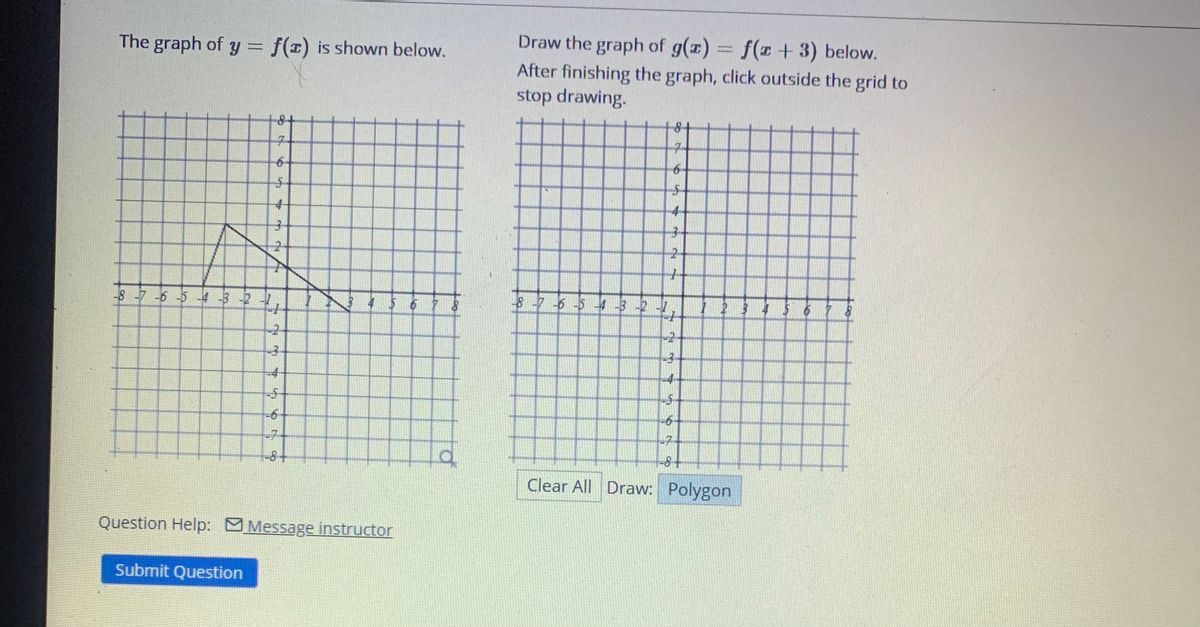



Answered The Graph Of Y F Z Is Shown Below Bartleby




Z The Zeros Of The Quadr Descubre Como Resolverlo En Qanda



Www2 Math Binghamton Edu Lib Exe Fetch Php Calculus Math 323 Exam 2 Practice Exams Solutions Pdf



Dr Moretti S Mathematica Notebooks Calculus 3




One Man S Funnies Mathematical Equations Of Love Heart Penis And The Boomerang




On A Graph Paper Draw The Graph Of Linear Equation 3x 2y 4 And X Y 3 0 Also Find Their Point Of Brainly In
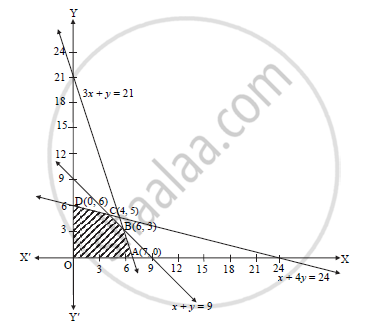



Maximize Z 3x 5y Subject To Mathematics And Statistics Shaalaa Com




Systems Of Linear Equations




3 5 Graphs In Three Dimensions Objective To
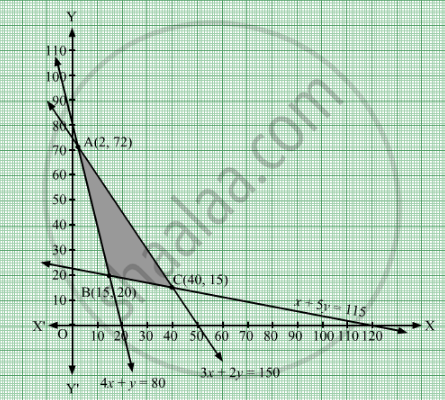



Solve The Following Linear Programming Problem Graphically Minimize Z 6 X 3 Y Subject To The Constraints 4 X Y 80 X 5 Y 115 3 X 2 Y 150 X 0 Y 0 Mathematics Shaalaa Com
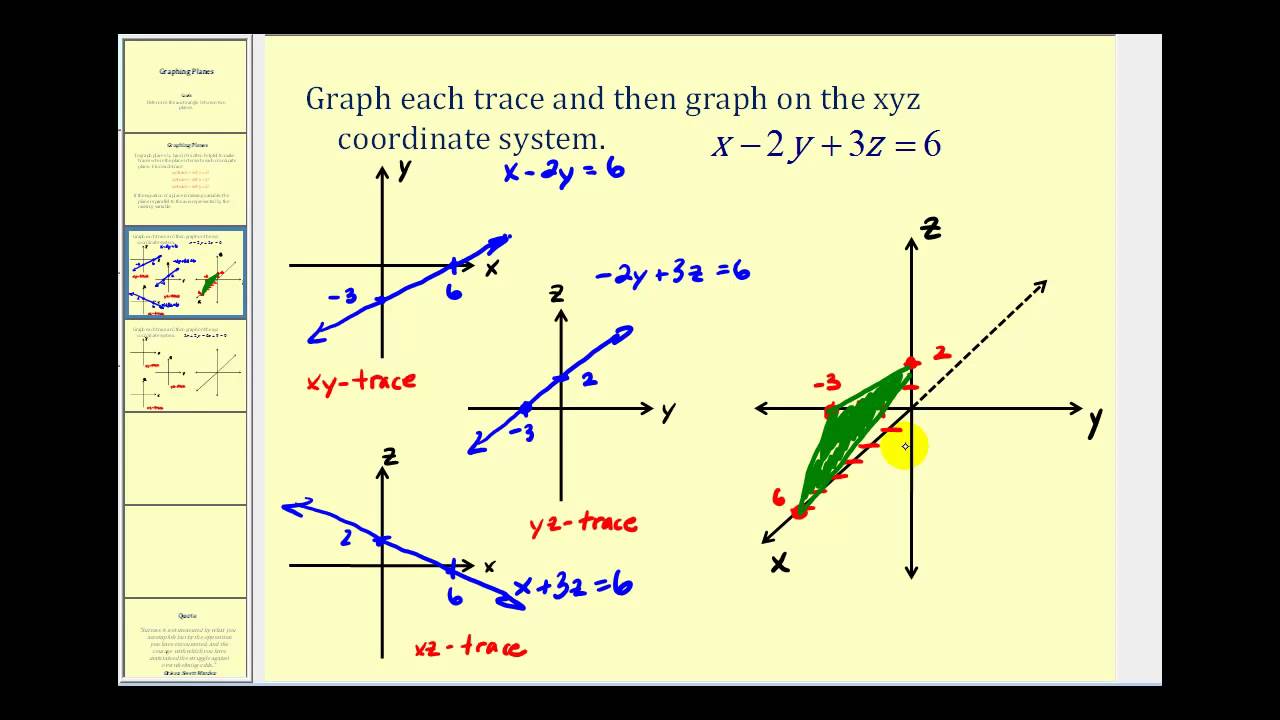



Graphing A Plane On The Xyz Coordinate System Using Traces Youtube



Eigenvalues Of Zero Divisor Graphs Of Finite Commutative Rings Springerlink
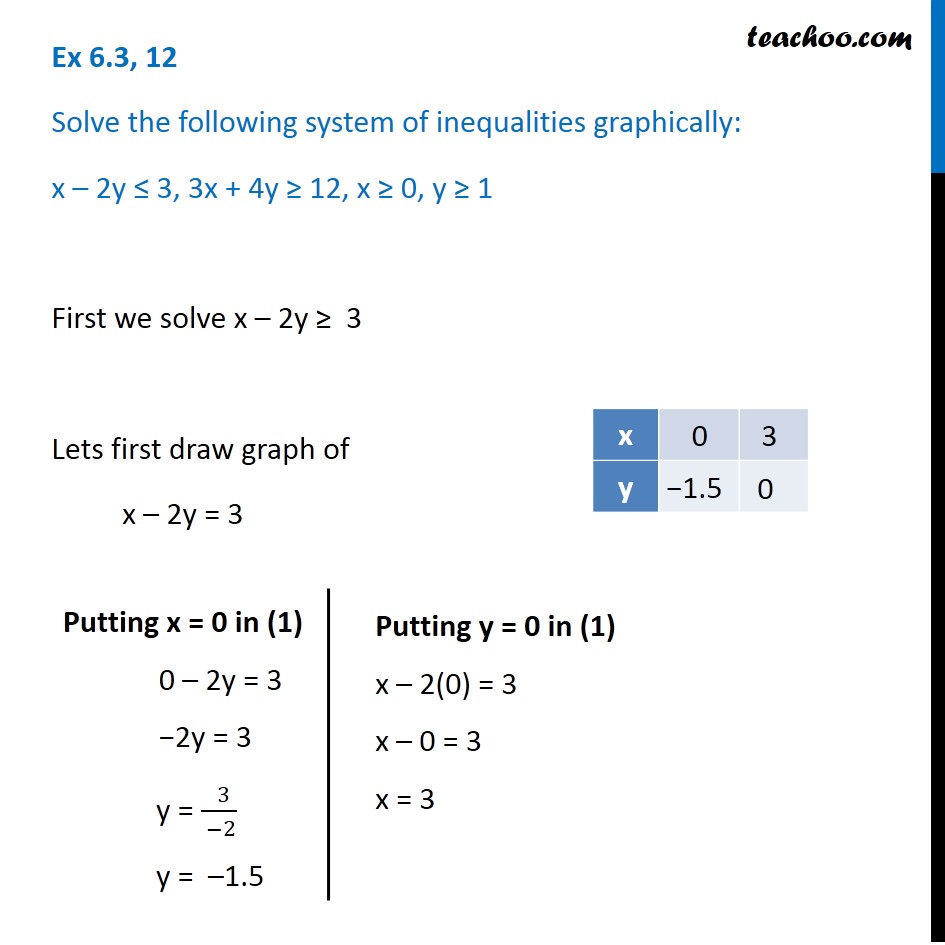



Ex 6 3 12 Solve Graphically X 2y 3 3x 4y 12



Solve The Following Linear Programming Problems Graphically Class 10 Maths Cbse



1



Sites Ualberta Ca Mackall Lab Material 9 Math 9 quiz 3 Pdf



Http Www Math Drexel Edu Classes Calculus Resources Math0hw Homework11 7 Ans Pdf



Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables And Surfaces



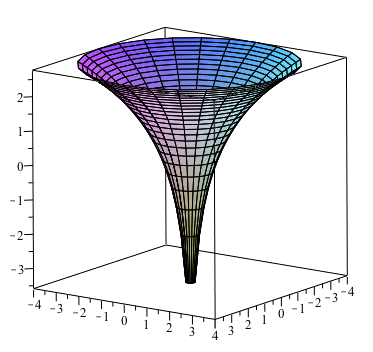
Solved Try To Sketch By Hand The Curve Of Interse



How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic




Maximise Z 3x 2y Br Subject To X 2yle10 3x Yle15 X Yge0




X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Graph Novocom Top



Mathematics Calculus Iii




Let S Be The Denote The Portion Of The Graph Of The Function Z X2 Y2 Between The Heights 3 And Homeworklib



1
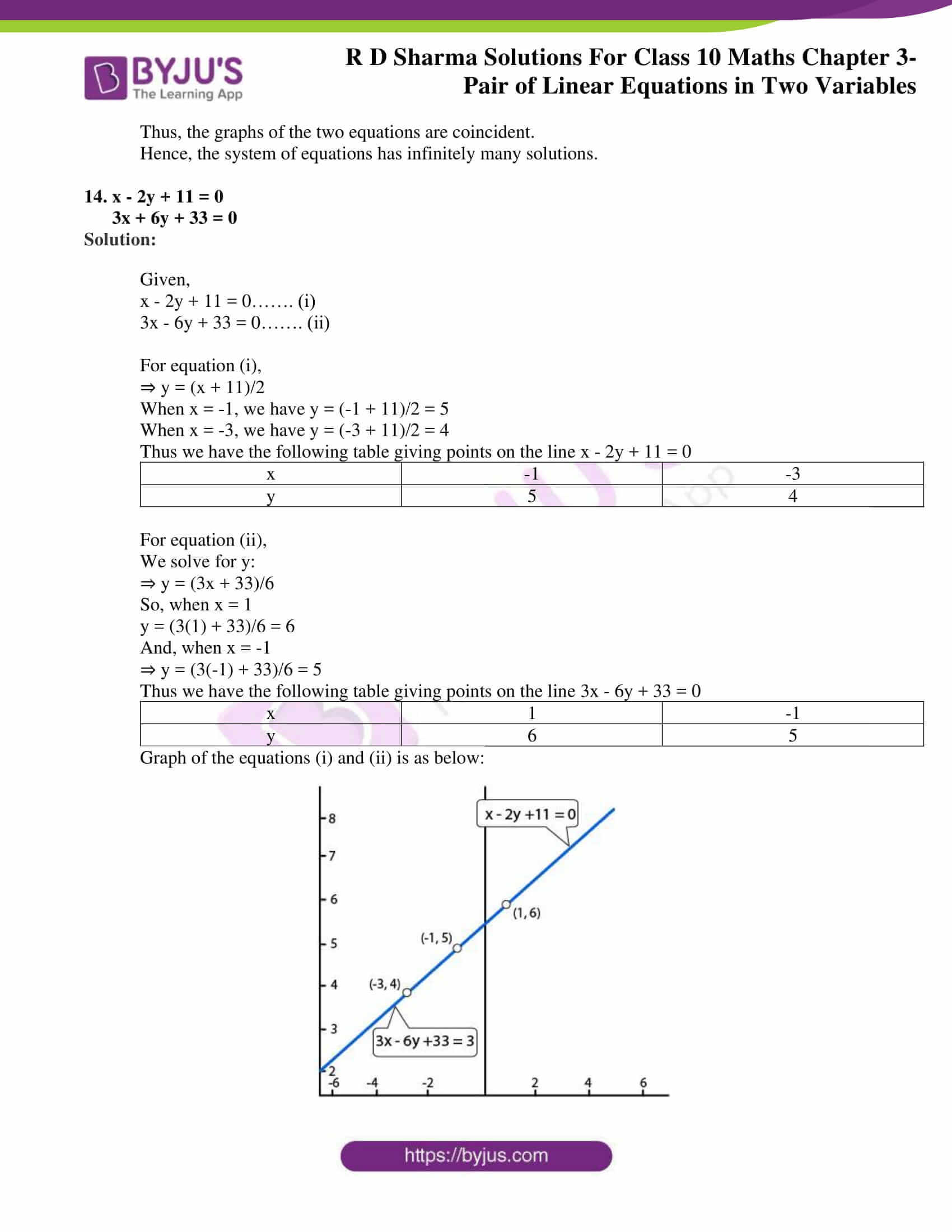



Rd Sharma Class 10 Solutions Maths Chapter 3 Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Exercise 3 2




3 5 Graphs In Three Dimensions Objective To



Http Abel Math Harvard Edu Archive 21a Spring 09 Pdf Midterm1 Solns Spr08 Pdf




Graph Xyz With Vertices X 2 3 Y 3 2 And Z 4 3 And Its Image After The Translation X Brainly Com




Plot Of A Portion Of The Variety X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Z 3 0 Download Scientific Diagram



What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿